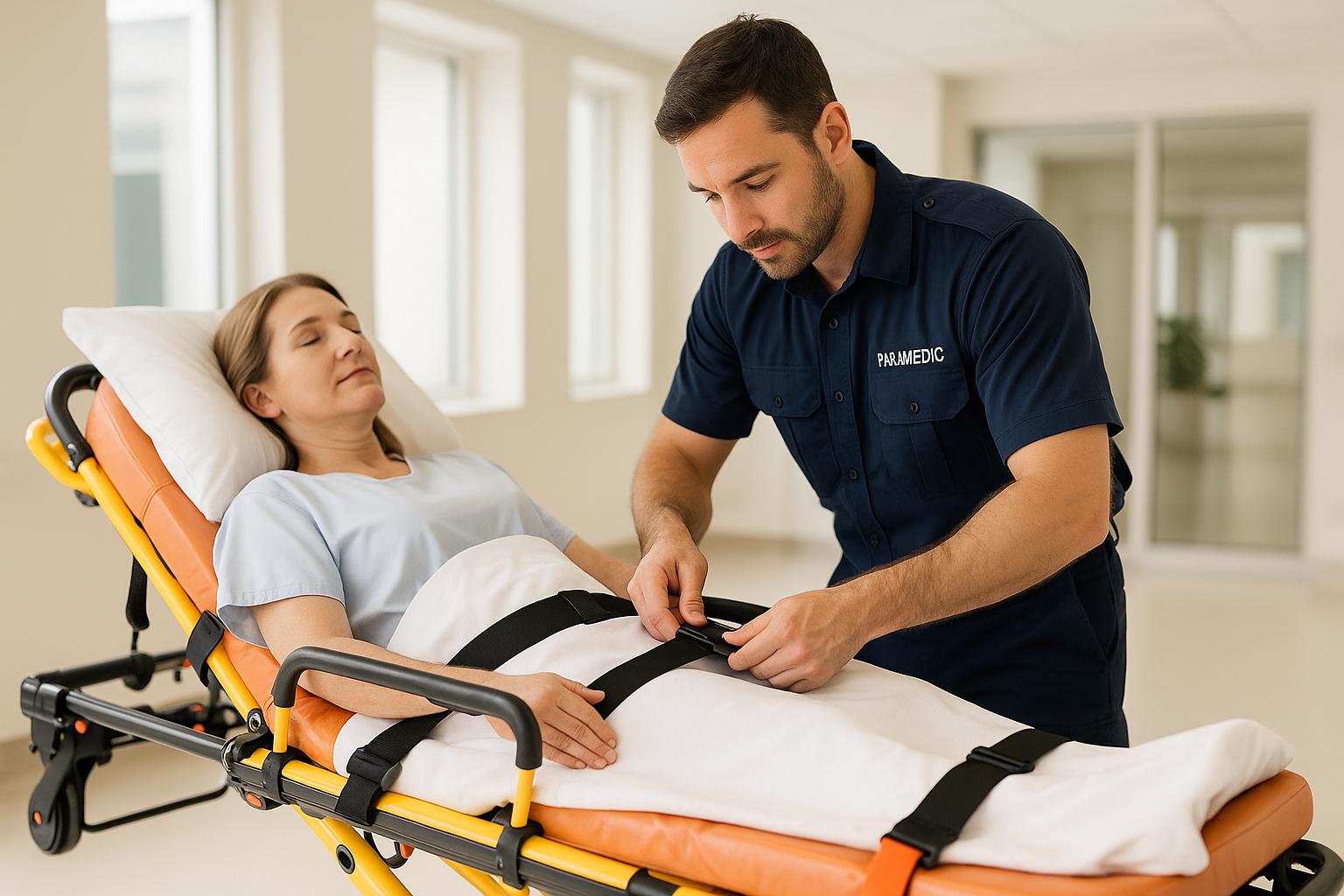
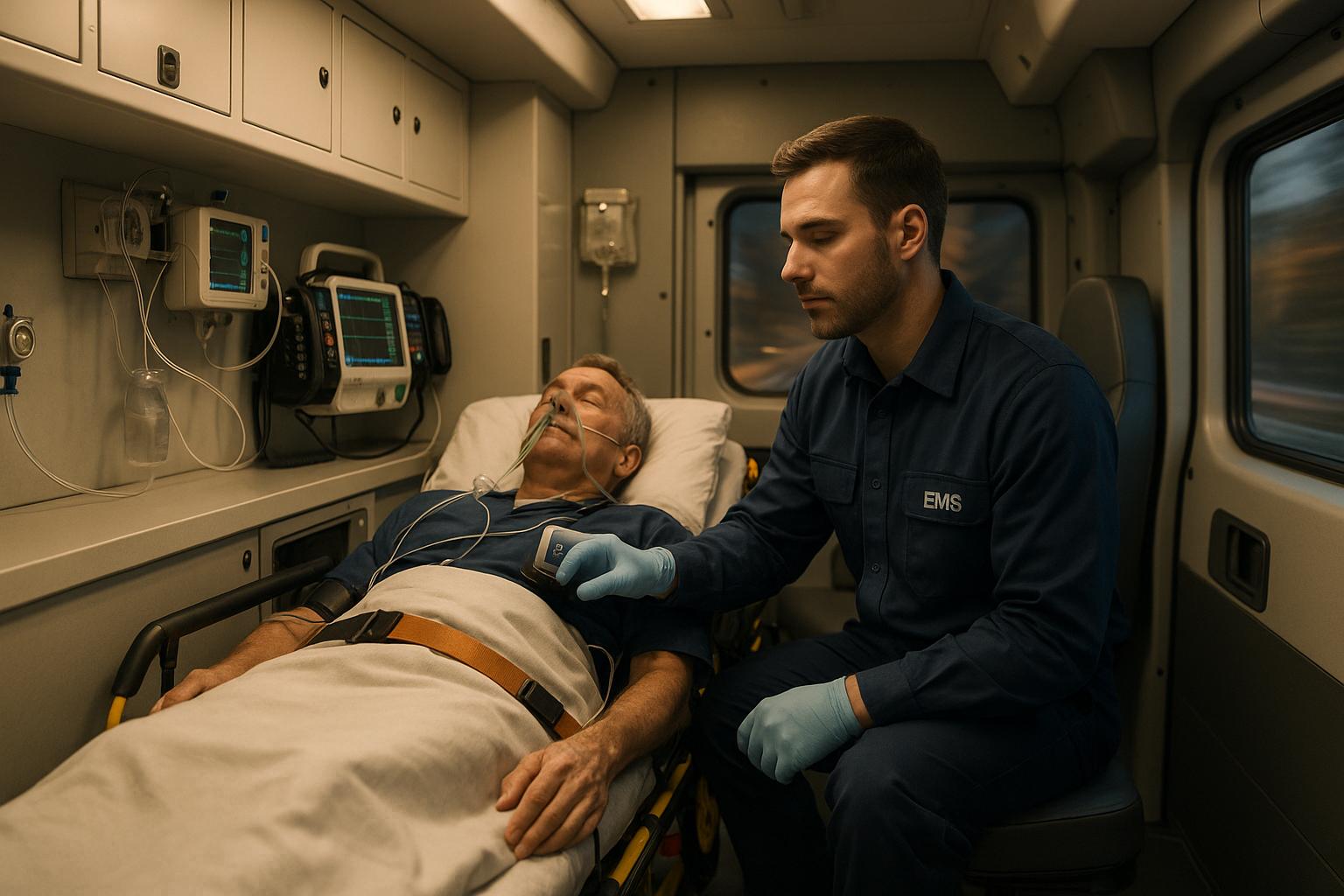
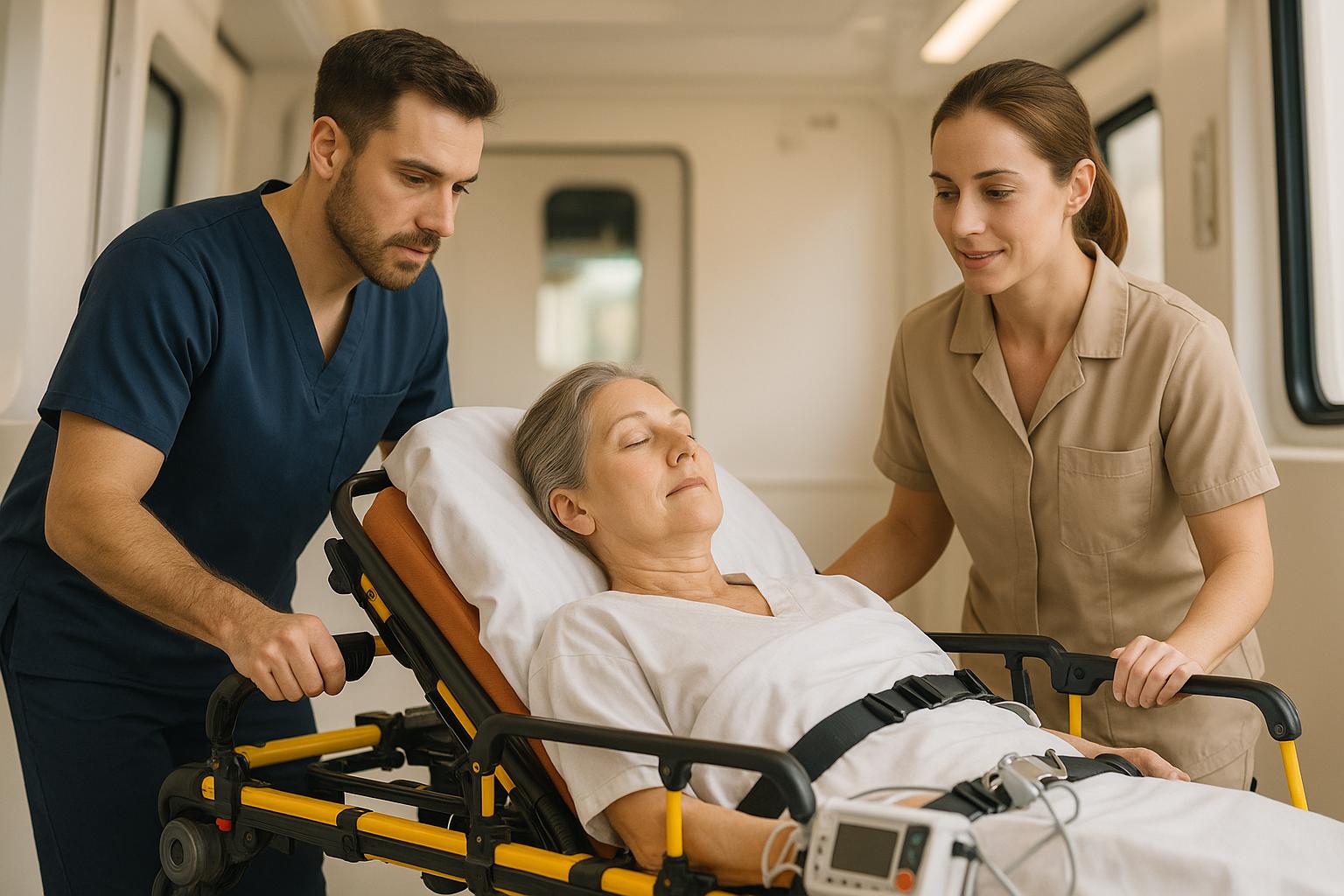
Stretcher transport ensures patients with limited mobility receive care safely and comfortably. However, safety depends on strict protocols, well-maintained equipment, and trained staff.
Key takeaways:
- Regulations: U.S. standards (FDA, FMVSS, AST) and global certifications (ISO, CE) ensure stretcher safety, from design to operation.
- Equipment Features: Modern stretchers include side rails, safety straps, anti-skid wheels, hydraulic systems, and bariatric options to meet diverse needs.
- Pre-Transport Checks: Inspect stretchers, secure IV lines, and disinfect equipment to prevent risks during transfers.
- Vehicle Safety: Transport vehicles must have secure mounting systems, braking systems, and climate control to ensure patient stability.
- Training: Staff must be skilled in patient handling, emergency response, and equipment operation, with regular assessments to maintain expertise.
Ambulance Stretcher: A Comprehensive Guide to Proper Usage: Part 1
Regulatory Standards and Guidelines for Stretcher Transport
In the U.S., stretcher transport is governed by a mix of federal and industry standards designed to prioritize patient safety. These regulations set minimum safety requirements for transport providers, addressing both equipment specifications and operational practices. This framework lays the groundwork for understanding the essential features and procedures that ensure safe and effective patient transport.
International and U.S. Safety Standards
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees medical devices, including hospital stretchers, to ensure they meet stringent safety and performance criteria. On a global scale, standards like ISO 1865 outline requirements for patient handling devices used in medical transport. Many manufacturers aim for certifications such as ISO, CE, and FDA to meet both domestic and international expectations.
Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards (FMVSS) come into play when stretchers are part of transport vehicles, covering everything from secure fastening systems and hydraulic lifts to lighting, braking systems, and overall vehicle safety. Additionally, the Association of Surgical Technologists (AST) has developed detailed Standards of Practice for patient transportation, offering healthcare facilities a framework for creating safe transfer protocols.
These standards influence daily practices, from equipment inspections to transport procedures, ensuring safety remains a top priority.
Material and Design Requirements
Regulatory standards play a key role in shaping the design of modern stretchers, ensuring they meet safety and functionality needs.
Today's stretchers often feature collapsible side rails, central locking systems, and anti-skid wheels. Pediatric models are equipped with higher side rails for added protection. Locking mechanisms on wheels prevent unwanted movement during transfers, further enhancing safety.
Weight capacity is a crucial consideration in stretcher design. While standard stretchers handle most patient transport scenarios, bariatric models are built to support weights exceeding 1,000 pounds. These variations cater to diverse patient needs and clinical situations.
Hydraulic systems are another important feature, allowing smooth height adjustments that reduce caregiver strain and improve patient comfort. Many hydraulic frames offer four-sided access, enabling caregivers to assist patients from any angle - especially useful during transfers between beds and stretchers.
To maintain hygiene, stretchers are designed with minimal joints and washable surfaces, making them easier to disinfect. Regular inspections are vital to ensure ongoing safety. Weekly checks typically focus on wheels, brakes, and securement systems. Vehicles used for transport also undergo routine maintenance and multi-point inspections, which cover braking systems, tires, seatbelts, hydraulic lifts, lighting, and sanitation.
Safety Features of Stretcher Equipment
Modern stretchers come equipped with both fundamental and advanced safety features to ensure patients remain secure during transport.
Basic Safety Mechanisms
Side rails are a primary safety feature, creating a barrier that helps prevent patients from falling during transport. For pediatric patients, these rails are designed to be higher to account for unpredictable movements, ensuring children can't climb over or accidentally fall out.
Safety straps are another critical component. For adults, thigh straps are typically positioned about two inches above the knees, while pediatric patients may require additional restraints for added security. These straps must be snug enough to hold the patient securely without restricting breathing or causing discomfort.
Wheel locking mechanisms are essential to keep the stretcher stationary during patient transfers. Whether loading into a vehicle or moving between surfaces, engaging the wheel locks is a necessary step to prevent unwanted movement. The wheels themselves are designed to navigate various surfaces while maintaining stability.
A securely attached mattress is vital to prevent shifting that could destabilize the patient during transport. Ensuring the mattress is firmly fastened to the stretcher frame is a basic yet crucial safety measure.
These foundational features form the backbone of stretcher safety, allowing for the integration of more advanced technologies.
Advanced Safety Features
Electric and hydraulic height adjustments make it easier to position stretchers at optimal levels for safe patient transfers and loading. This reduces strain on medical staff and minimizes unnecessary patient movement during the process.
Shock absorption technology is another innovation that enhances patient comfort and safety. By cushioning impacts and reducing vibrations, it helps prevent disorientation, nausea, or secondary injuries caused by rapid or uneven movement.
To accommodate heavier patients, bariatric stretchers have been developed with reinforced frames, wider platforms, and enhanced weight capacities. While standard stretchers typically support up to 450 pounds, bariatric models are designed to handle 600 pounds or more, all while maintaining the same essential safety features.
Material selection for stretcher frames is carefully considered to balance durability and maneuverability. Frames need to be lightweight enough for easy handling but strong enough to withstand frequent use. Additionally, materials are chosen for their resistance to corrosion and wear from regular cleaning and disinfecting, ensuring long-term reliability.
Some stretchers also incorporate built-in features like oxygen cylinder holders and IV poles. These eliminate the need for separate equipment, reducing the risk of items shifting or falling during transport while keeping medical tools accessible and secure.
The weight of the stretcher itself, which can range from 100 to 700 pounds depending on its design and features, also impacts maneuverability in tight spaces like hospital corridors and elevators.
These advanced safety features work in tandem with basic mechanisms to ensure patient stability and comfort during transport. They also highlight the importance of thorough pre-transport checks. Before every patient transfer, personnel must inspect wheel locks, verify the integrity of safety straps, confirm side rail functionality, and ensure all accessories are securely mounted. These steps are critical for maintaining compliance with regulatory standards and ensuring safe, reliable performance.
Pre-Transport and Transit Safety Procedures
Ensuring patient safety during transport starts well before moving the stretcher. A structured approach to preparation and handling helps healthcare workers make the process as secure and comfortable as possible.
Pre-Transport Equipment and Patient Checks
The first step in a safe transport is correctly positioning the stretcher. Place it next to the patient’s bed, slightly lower than the bed's height, to allow for a smooth transfer and reduce the risk of sliding or falls. Always lock the wheels on both the stretcher and the bed (if it has wheels) before beginning the transfer.
A thorough equipment check is essential. Confirm that the side rails can be raised and locked, safety straps are functional and accessible, and the mattress is securely in place. These features are critical for both patient safety and the smooth operation of the stretcher.
Pay close attention to any medical attachments. IV lines, catheters, monitoring cables, and drainage tubes must be securely positioned and fully operational. Keep IV bags and collection containers away from the patient’s head to prevent accidental disconnections or contamination. Oxygen tanks should be fastened securely in their designated holders.
The stretcher’s weight capacity is another key safety consideration. Most modern stretchers can handle between 500 and 750 pounds, accommodating the majority of patients. For heavier patients, specialized stretchers with capacities over 1,000 pounds should be available. Some newer models even feature smart weight sensors that can detect the patient’s weight and assist with safe lifting protocols and accurate medication dosing.
Proper patient positioning is just as important. Use adequate padding to support the head, arms, and legs, reducing the risk of pressure injuries. For patients with potential spinal injuries, immobilization is crucial - equipment like scoop stretchers, which split vertically, can minimize unnecessary movement. Pediatric patients require extra care, with crib stretchers featuring high rails and specialized padding to keep them secure during transport.
Infection control is a critical part of preparation. Visually inspect the stretcher to ensure it has been disinfected after its previous use. Stretchers must be sanitized after every patient, with deep cleaning required after exposure to blood or bodily fluids, following CDC guidelines. Effective disinfection relies on allowing the cleaning agent to remain on surfaces for the recommended duration to eliminate pathogens.
Once the equipment and patient are prepared, the focus shifts to safe handling practices during the actual transfer.
Safe Handling and Transport Practices
With the equipment ready, it’s time to concentrate on careful handling during the transfer and transit. Clear communication among staff is vital, and using transfer devices can help reduce strain and prevent sudden movements that could harm either the patient or the caregivers.
Once the patient is on the stretcher, raise the side rails and fasten safety straps. These should secure the patient without causing discomfort or restricting breathing. In tight spaces or when handling heavier patients, a two-person protocol is recommended for lifting, loading, and positioning.
During transit, ensure the stretcher is firmly secured to the vehicle’s mounting system. Keep the side rails raised throughout the journey, especially during turns, acceleration, or deceleration, to maintain stability. Lower the rails only when the patient is fully supported and ready for transfer. Adjust the vehicle’s temperature and ventilation to meet the patient’s medical needs, enhancing their comfort and stability.
The stretcher’s weight also affects handling. Stretchers can weigh anywhere from 100 to 700 pounds, so navigating hallways, elevators, and loading into vehicles requires careful planning. Staff should consider these factors when selecting routes and coordinating the transfer.
After the transport, post-transport protocols ensure the stretcher is ready for the next use. Clean all touch surfaces, restraints, and components with healthcare-grade disinfectants. Recheck the equipment to confirm it’s in proper working order. This step not only supports infection control but also ensures the stretcher is immediately available for the next patient, maintaining a high standard of safety and efficiency.
sbb-itb-a0ce227
Vehicle Compatibility and Secure Transport Systems
Properly equipping vehicles for patient transport is essential to ensure both the safety of the patient and the stability of the stretcher in transit. Vehicles must be designed with secure mechanisms and features that align with federal and industry safety standards, working in harmony with stretcher designs to maintain stability. Below, we explore how vehicles can meet these strict compatibility and safety requirements.
Stretcher Compatibility with Transport Vehicles
Stretchers come in a wide range of sizes and weights, typically ranging from 100 to 700 pounds, which directly impacts how they function within a transport vehicle and the vehicle’s load capacity. To ensure compatibility, the stretcher must fit securely in the vehicle’s designated space, with enough room to accommodate the patient’s length and any required medical equipment. Healthcare facilities should carefully select stretchers that are appropriately sized for their patients while ensuring they can be securely positioned within the vehicle. For bariatric patients, specialized stretchers with higher weight capacities are necessary, as standard models may not provide adequate support.
Transport vehicles must also be equipped to safely house essential medical equipment, including IV poles, oxygen tanks, and monitoring devices. These items need secure integration to prevent movement during transit. Hydraulic lifts are another critical feature, enabling safe and efficient loading and unloading of stretchers, while secure mounting systems ensure that both the stretcher and mattress remain firmly locked in place. Regular inspections of these systems are necessary to maintain their reliability.
In-Transit Stability Systems
Once the stretcher is properly fitted, securing it during transit becomes the top priority. Before any patient transfer or transport begins, all wheels on the stretcher must be locked to prevent movement. Many modern stretchers are equipped with anti-skid wheels and central locking systems that enhance stability during transportation. Anti-skid wheels are particularly effective at minimizing sliding or shifting caused by sudden braking, acceleration, or turns, while central locking systems provide an additional layer of security.
Given that some stretchers can weigh as much as 700 pounds when loaded, even slight uncontrolled movement can pose serious risks, including patient injury or equipment damage. Properly locking the wheels and engaging central locking systems help protect patients and ensure that medical lines, catheters, and monitoring devices remain undisturbed during transit.
Transport vehicles must also include secure mounting brackets, restraint points, and climate control systems to maintain both stability and patient comfort while in motion. Routine multi-point inspections of transport vehicles are vital, covering critical systems such as brakes, hydraulic lifts, restraint mechanisms, lighting, heating, ventilation, and sanitation. These inspections ensure that all securing components are functioning as intended. Additionally, safety belts and straps provide extra stabilization, reducing the risk of falls or injuries during vehicle movement.
To meet safety standards, all vehicles and auxiliary equipment used for patient transport must comply with federal, state, and local inspection and maintenance requirements. Many stretcher manufacturers certify their products to meet ISO, CE, and FDA standards, ensuring they meet global benchmarks for hygiene, safety, and performance. Regular maintenance schedules are crucial for preventing equipment failures, and transport providers should exceed the industry minimum for maintenance frequency to ensure reliability. Keeping detailed records of inspections and maintenance for both stretchers and vehicles not only ensures compliance with safety regulations but also helps identify potential problems before they escalate into critical issues.
Training and Maintenance for Safety Standards
Ensuring safety in stretcher transport hinges on strict adherence to equipment protocols, comprehensive staff training, and consistent maintenance. These elements work together to protect both patients and transport teams, creating a secure environment for everyone involved.
Staff Training and Certification Requirements
Healthcare workers tasked with stretcher transport must undergo thorough training to handle patients safely and effectively. Certifications in first aid and CPR are essential, equipping staff to respond to medical emergencies during transit. Additionally, training in proper patient transfer techniques is critical for preventing injuries. This includes mastering correct body mechanics and using transfer devices appropriately, especially when assisting patients with diverse medical needs or physical conditions.
Operating various stretcher types also requires specialized knowledge. Staff must learn how to adjust hydraulic systems, engage braking mechanisms, and correctly use safety restraints. For hydraulic stretchers, understanding how to manage height controls and pressure indicators is particularly important. These systems significantly reduce manual lifting, which helps minimize the risk of back injuries for staff.
Risk assessment training further enhances safety during transport. Teams need to evaluate factors such as a patient’s medical condition, mobility limitations, size, weight, and cognitive status. They must also account for environmental challenges like narrow hallways, stairs, uneven surfaces, and poor lighting, all of which can complicate movement.
ReliaWheels, for instance, ensures its drivers are fully certified and trained in areas like wheelchair securement, stretcher operation, passenger assistance, and emergency response. Every stretcher transport includes at least two trained professionals to manage lifting, loading, and positioning safely. This approach prevents strain, tipping, or sudden movements that could put patients at risk.
Clear communication among team members is another key component of safe patient transfers. Whether navigating tight spaces or addressing complex medical needs, staff must coordinate their actions effectively. Organizations should also document staff certifications and implement periodic refresher training. Competency assessments, which might include written exams or practical demonstrations like securing patients or locking stretcher wheels, help ensure that staff maintain their skills. Regular audits and performance reviews further reinforce adherence to safety protocols.
Equipment Inspections and Maintenance Schedules
Just as skilled personnel are essential, so too is the consistent upkeep of equipment. Routine inspections and maintenance are crucial to ensure that stretchers remain safe and functional for repeated use. Before each transport, equipment should be checked thoroughly. This includes verifying that wheel locks are secure, the mattress is stable, and side rails operate smoothly. Safety straps must be inspected for tears or wear, and hydraulic or powered systems should be tested to confirm height adjustments are stable and reliable. The stretcher frame should also be examined for signs of stress or corrosion.
Other components, such as IV poles, oxygen tank holders, and accessory attachment points, need regular checks to ensure they are secure and functioning correctly. Any defects should be documented and repaired immediately to avoid equipment failure during transport.
After every use, all surfaces - including the mattress, frame, rails, and attachment points - must be disinfected using healthcare-grade cleaners that meet public health standards. Stretchers designed with fewer joints and washable surfaces make this process more efficient and thorough.
Beyond daily cleaning, stretchers require regular mechanical inspections to identify wear and tear. Hydraulic systems should be checked for leaks or pressure loss, while wheels and braking mechanisms need periodic lubrication and testing to ensure smooth operation. Mattresses showing signs of wear should be replaced promptly to maintain proper support and patient safety.
Many facilities follow a structured schedule for equipment maintenance, often conducting detailed evaluations on a quarterly or semi-annual basis. During these checks, stretchers are removed from service for thorough inspections by qualified technicians. Preventive maintenance like this helps avoid unexpected breakdowns and ensures continuous safe operation.
Detailed maintenance logs play a critical role in compliance and accountability. These logs should document inspection dates, components checked, identified defects, completed repairs, and the personnel responsible. Similarly, maintaining records of staff training, certifications, and incident reports strengthens the overall safety program.
While stretcher manufacturers adhere to global standards like ISO, CE, and FDA guidelines to ensure hygiene, safety, and performance, ongoing maintenance is vital to uphold these standards throughout the equipment’s lifespan. Regular care and attention to detail ensure that safety remains a top priority.
ReliaWheels: Safe Stretcher Transport in Cleveland
ReliaWheels takes safety seriously, embedding rigorous protocols into every part of its stretcher transport services in Cleveland. Whether it’s a trip to a dialysis appointment, a nursing home, or a medical facility, the company combines industry-standard safety practices with specialized equipment to meet the needs of patients requiring stretcher transport.
To ensure safe travel, all drivers are licensed and certified in CPR, equipping them to handle medical emergencies during transit. This level of preparation underscores ReliaWheels' dedication to patient safety.
The vehicles are purpose-built for stretcher transport, designed to securely accommodate modern stretchers while maintaining stability on Cleveland's diverse roadways. Each vehicle undergoes routine inspections to ensure all equipment is functioning properly before a patient is loaded. Additionally, the wheelchair-accessible designs offer flexibility for varying dimensions and weight requirements, ensuring a snug and secure fit for stretchers.
ReliaWheels emphasizes meticulous equipment maintenance. Every piece of equipment is carefully inspected before use, minimizing the risk of malfunctions that could jeopardize patient safety.
Beyond equipment checks, the company conducts thorough patient evaluations before transport. Vital signs, mobility, and any special needs are reviewed to ensure the safest handling possible. For patients with complex medical requirements - such as IV lines, oxygen support, or specific positioning - ReliaWheels collaborates with healthcare providers to fully understand the patient’s needs and prepare accordingly.
ReliaWheels offers comprehensive door-to-door service, ensuring patients reach dialysis centers, nursing homes, or medical facilities safely and on time. For those needing specialized care outside Cleveland, the company also provides long-distance stretcher transport.
Communication is a cornerstone of ReliaWheels' safety strategy. The team works closely with healthcare facilities to understand each patient’s clinical requirements. This includes verifying that any hospital-provided equipment, like portable oxygen tanks or monitors, can be safely secured during transit. The door-to-door service ensures careful monitoring and proper positioning throughout the journey, with clear protocols in place to contact emergency services or the receiving facility if a patient’s condition changes unexpectedly.
ReliaWheels also prioritizes vehicle and equipment upkeep to deliver reliable service. Regular inspections catch potential issues before they impact patient care, while scheduled maintenance ensures that all systems operate at peak efficiency.
For families and healthcare providers in Cleveland, ReliaWheels offers a stretcher transport solution that blends safety with specialized care. With trained staff, well-maintained vehicles, and a focus on patient well-being, the company provides peace of mind for every journey, reflecting the highest standards in the industry.
Conclusion
Safety standards in stretcher transport go far beyond just meeting regulations - they create a system designed to protect patients at every step of their journey. From the moment equipment is inspected to the final arrival at a medical facility, each safety measure works in harmony with the others, creating multiple layers of protection. This interconnected approach reflects the strategies discussed throughout this article: when regulatory guidelines, equipment design, staff training, and maintenance protocols align, even if one element falters, others step in to safeguard the patient.
Healthcare facilities and transport providers carry the responsibility of upholding these standards. Stretchers must be handled with care, critical components inspected regularly, and strict infection control measures applied using healthcare-grade disinfectants after every use.
At the heart of these protocols is a commitment to patient dignity. These safety measures ensure that all patients, regardless of their physical condition or socioeconomic background, receive equal and respectful care. By standardizing safety requirements, the healthcare system helps close gaps in care quality and reduces risks for vulnerable groups who might otherwise face delays or inadequate attention.
A well-trained team is essential to this process. Professionals skilled in handling techniques, emergency responses, and patient assessments create an environment where safety protocols are not just followed but fully understood. This understanding fosters a culture of care that prioritizes patient well-being. For patients and their families, knowing that safety belts are securely fastened, medical lines are double-checked, and vehicles are meticulously maintained offers peace of mind. When patients share specific medical needs or concerns ahead of time, providers can prepare the right equipment and support to deliver personalized care tailored to individual requirements.
Ultimately, these safety standards reflect the broader mission of healthcare: ensuring that every patient receives equitable and dignified care. By blending regulatory standards with compassionate practices, the stretcher transport industry continues to improve patient experiences. Every inspection, protocol, and training effort strengthens a system where patients can travel with confidence, comfort, and the protection they deserve.
FAQs
What safety features should a modern stretcher have for secure patient transport?
Modern stretchers come equipped with essential safety features designed to protect patients during transport. Key features include adjustable safety straps to secure patients, shock-absorbing frames for a smoother experience, and locking wheels to prevent unwanted movement during loading or unloading. Another important feature is height adjustability, which helps reduce strain on caregivers and ensures safer patient transfers.
To guarantee reliability, stretchers for medical transport should adhere to industry standards and undergo regular maintenance. Companies like ReliaWheels emphasize these safety measures, providing secure and comfortable transport services for patients needing specialized care in Cleveland, Ohio.
What safety standards are followed for stretcher transport in the U.S.?
In the U.S., stretcher transport services operate under rigorous safety protocols and industry guidelines designed to protect patients during transit. These guidelines address every detail, from securely fastening stretchers to conducting vehicle safety inspections and ensuring staff are well-trained in patient handling techniques.
Specialized providers, particularly those offering non-emergency medical transportation (NEMT), go a step further by equipping their vehicles with wheelchair-accessible features and secure stretcher systems. On top of that, trained professionals are available to provide additional care and support, prioritizing both the comfort and safety of patients throughout their journey.
What qualifications and training do staff need to ensure safe stretcher transport?
When it comes to stretcher transport, staff need specialized training and certifications to prioritize patient safety. This training covers essential skills like proper lifting techniques, securely positioning patients, and efficiently operating stretcher equipment.
Additionally, these professionals are prepared to manage medical emergencies that may arise during transit. They also adhere to strict industry safety standards and protocols, ensuring patients experience care that is not only safe and dependable but also compassionate throughout their journey.
.png?width=2931&height=601&name=Purple%20and%20Green%20Paper%20Music%20Event%20Banner%20(7).png)




